Circular Knife Blade
You need more than just a industrial circular knife blade, you need a veteran supplier with 20 years in the field to build your brand and increase your profits. Let PASSION help you achieve business success.
The Circular Knife Blade PASSION Offers You
Circular knife blades are widely used in industries from cardboard and tobacco to paper, packaging, and metal foil slitting. Whether you need standard or custom sizes, our 20 years of industry experience ensures precise solutions for your requirements.
Some Circular Knife Blades on Display
Over the past 15 years, we have produced nearly 5,000 industrial knife types, with circular knife blades making up about 45%. We offer extensive customization, supporting branded machine knives as well as drawing-based or material-supplied processing. Here are some recent examples.
























Let's Talk About Your Cutting Needs
Please provide the size,thickness and hardnessus of the material you want to slitting, along with the functons you need (e.g., full cut, half cut, indentation, grooving, etc.) With this information, we will quickly get back to you with a detailed solutions and quotes. Act Now

What Is A Circular Knife Blade?
Circular slitter blades are tools to cut sheets into strips or smaller sheets of the desired width. These blades are highly versatile and can be used for various applications, such as cutting paper, textiles, and metal.
Circular slitting blades are made from generally carbide or high carbon steel and are designed to be mounted on rotating machines. Circular slitting blades come in a variety of sizes and shapes to suit different materials and applications. The most common type of circular slitting blade is the round cutter, which is a disk with a sharp edge that is used to cut materials.
In practice, these blades often operate in pairs as top and bottom knives in a ‘shear slitting’ configuration, functioning like high-precision scissors. The final cut quality depends on the precise setup of the horizontal clearance and vertical overlap between these blades. The blade’s specific geometry, including its bevel angle and surface finish, is also critical for achieving a clean, burr-free cut while maximizing its operational life.
What Are The Types Of Circular Knife Blades?

Razor Slitting Blades
Application: Ideal for cutting thin materials such as films, foils, and laminates.
Features: Provides a clean, burr-free cut; commonly used for high-speed applications.
Material: Usually made of hardened steel or tungsten carbide for durability.

Score Slitting (Crush Cut) Blades
Application: Used for cutting thicker, tougher materials like rubber, foam, and some textiles.
Features: Applies pressure to fracture material along a line. Can generate dust and a rougher edge.
Material: Made from HSS or carbide with a precisely rounded edge for durability and effective cutting.

Shear Slitting Blades
Application: Ideal for cutting paper, cardboard, nonwoven materials, and some metals.
Features: Uses paired blades in a scissor-like action, providing precise cuts with minimal dust or burr.
Material: Made from tool steel (e.g., D2), high-speed steel, or carbide for long-lasting sharpness.

Perforating Blades
Application: For creating perforations in materials like paper, film, or foil, commonly used in packaging and labeling.
Features: Produces a series of small cuts to make materials easy to tear along a line.
Material: Manufactured from high-speed steel or carbide, with a customized tooth pattern.

Carbide-Tipped Blades
Application: Used in heavy-duty or abrasive materials, providing superior wear resistance for extended service life.
Features: Offers superior cutting performance and durability for high-production settings.
Material: Tungsten carbide tips on a steel core. Combines carbide’s hardness with steel’s toughness.
Toothed Blades
Application: For saw-like cutting of challenging materials like fibers, dense plastics, and rubber.
Features: Tooth design provides aggressive cutting, helpful in challenging or dense materials.
Material: Made from tool steel or HSS. For maximum durability, teeth can be tipped with carbide.


Circular Knife Blade Tooth Configurations
The style of a blade’s edge determines its primary function and cutting performance. Choosing the right edge for a specific material is key to maximizing efficiency and cut quality. Below are some common edge styles.



A Wide Range Of Quality Materials
The material is the heart of every high-performance industrial blade. The ultimate goal is a precise balance: hardness delivers superior wear resistance for a long-lasting, sharp edge, while toughness resists chipping and fractures, preventing costly production downtime. This critical balance directly impacts blade longevity, cut quality, and your overall profitability. Our experts help you navigate our wide range of materials to engineer a solution that provides optimal performance for your specific needs.
What Is A Circular Knife Blade Used For?
Circular knives are versatile tools essential to countless industries. Mounted on machinery, their rotary motion provides clean, efficient, and continuous processing. From dividing massive rolls of material to creating precise folds in packaging, circular blades perform a wide range of critical applications, including:
Cutting
Circular knives have a reputation for cutting different materials quickly, stably and completely. Rotating blades mounted on stationary machines make clean, downward cuts in materials ranging from high-density concrete to thin textiles. Circular knives offer a good all-around solution in applications dealing with a wide range of materials.
Trimming
Trimming a variety of products with a thin, precise blade makes them fine and accurate, helping to increase productivity and improve the quality of the processed product. Circular knives can trim materials such as fabric, leather, rubber, plastic and sheet metal.
Slitting
When people refer to industrial circular knives as “slitting knives”, they are usually referring to bevelled or toothless types of circular knives. These blades are the ideal blade type for slitting materials, which is one of their primary uses. Circular knives are suitable for a variety of slitting techniques, including hot knife, shaving and shearing.
Slicing
Circular knives offer the best solution for high workloads, such as repeatedly slicing material into uniform slices. Industries such as food processing, textile manufacturing, and metal cutting rely on circular knives for accurate, consistent, and productive slicing. Downward slicing with circular knives works well for cutting dense materials, as well as materials and fabrics that tend to slide.
Scoring
When you need fine precision tools, circular knives can help you realise the technique of scratch cutting. With the right combination of blade type and material, you can scribe on glass, stone, concrete, metal and a range of other materials. They are accurate enough to be used in precision scribing applications for paper products and packaging materials.
Creasing
When creasing fragile materials such as paper and packaging, you need a precise blade that produces a smooth, uniform crease. Rotary blades allow you to control the indentation and help you produce a high quality product.
Splitting
When you need to split materials without the risk of chipping, you need a blade that provides a clean, consistent cut and leaves a smooth finished product. Bevelled or toothless circular knives help split thin, lightweight materials, while circular knives with serrated edges make it easy to split denser, more durable materials. With the right configuration, your circular knives are ideal for splitting leather, rubber, paper, foam and more.
What Industries Use Circular Knife Blades?
Circular knives are one of the most widely used industrial machine blades. Their precision and durability make them essential across a diverse range of industries that process flexible and semi-rigid materials. Here are some key examples:

Food processing
Circular knives are one of the main cutting knives used in the food processing industry. Whether you’re trimming, slicing or cutting products such as meat, dairy, baked goods, seafood, fruits and vegetables, circular knives help you do it with precision.

Plastics
Make plastic processing faster and more efficient with plastic circular knives. With circular knives, you can cut, score, perforate and slit plastic products for high-quality results.

Foam
Foam processing needs can differ greatly depending on the type, density and hardness of the foam. Circular knives are the ideal knife for processing a wide range of foam products. Whether you need to cut, trim, slit, or slice, custom industrial circular knives can meet your needs.

Textiles, Non-Wovens And Leather
Circular knives are useful when cutting textiles and leather. The downward cutting precision blades can easily handle materials of various textures and thicknesses. Premium leather cutting blades split leather, while circular textile knives can perforate and trim different fabrics.

Converting: Film, Foil And Tape
In the converting industry, circular knives are critical for slitting wide rolls of flexible materials into narrower ones with perfect edges. This includes plastic films, adhesive tapes, labels, laminates, and thin metal foils like aluminum and copper.

Paper And Corrugated Products
When you need to prepare high workloads of paper products, corrugated cardboard, packaging materials and other products, circular knives are ideal for scoring and cutting. Choose a custom circular knives design to meet your paper processing needs.

Packaging
When processing packaging materials, you need a versatile and high-quality blade. A circular knife can precisely cut, trim, slit and split different packaging materials.

Composites And Fiberglass
Processing fibreglass and composite materials requires durable blades for precise, clean cuts and trimming. Industrial circular knives make precise cuts and help you achieve a wide range of fibre cutting techniques.
What Maintenance Is Required On Circular Knife Blades?
Proper maintenance is key to your circular blade’s performance, durability, and safety. A consistent routine extends blade life, reduces costly downtime, and ensures superior cut quality. Follow these steps to keep your blades in peak condition.

Regular Cleaning
Debris Removal: After each use, immediately remove any chips, residue, or material buildup using a soft brush or cloth. This carefully prevents residue from dulling the blade, increasing friction, and causing uneven cuts.
Cleaning Solution: Use a manufacturer-approved, industrial-grade cleaning solution for stubborn residues. Always avoid harsh, corrosive chemicals that can degrade the blade material or its coating.

Lubrication
Corrosion Prevention: In high-humidity environments, applying a light coat of food-safe or manufacturer-approved protective oil during storage can prevent rust. Ensure the blade is thoroughly cleaned before its next use.
Critical Note: Do NOT apply lubricants if the blade is used in food processing, medical, pharmaceutical, or other clean-sensitive industries, as this will contaminate the final product.

Professional Sharpening & Regrinding
Maintain Edge Geometry: Schedule periodic professional sharpening to ensure peak performance. Dull blades lead to poor cuts, increased cutting force, and higher energy consumption.
Why Professional Service is Crucial: Pros use CNC machines to restore precise angles and balance. NEVER use a bench grinder—it will permanently damage the blade’s temper and geometry.

Inspect for Wear and Damage
Check For Micro-Cracks And Chips: Visually inspect the cutting edge for any chips, micro-cracks, or irregularities that could compromise cut quality or lead to catastrophic failure. Use magnification if necessary.
Replace When Necessary: If significant wear or damage is found that cannot be corrected by professional sharpening, replace the blade immediately to maintain safety and operational efficiency.

Blade Alignment and Balance
Ensure Proper Mounting: Before installing a blade, ensure the blade, clamping collars, and machine arbor are perfectly clean. Any debris can cause misalignment and vibration, leading to poor cuts and premature wear.
Verify Alignment: Always verify the blade is properly aligned with the machine’s cutting path according to the equipment manufacturer’s specifications. A well-mounted blade maintains its factory balance, preventing vibration.

Storage
Dry Environment: To prevent rust and corrosion that dull the blade, always store blades in a clean, dry, and temperature-controlled area. Avoid high humidity and extreme temperature swings which can degrade the steel over time.
Protective Covers: Protect both the blade and your staff. Store each blade in a dedicated case or protective sleeve. This shields the precision-sharpened edge from accidental damage and is critical for preventing serious injury during handling.
Usage Protocols
Correct Operation: Operate within the recommended speed and material guidelines to avoid unnecessary strain.
Avoid Overheating: Allow blades to cool if they become excessively hot during prolonged use, which can alter their structural integrity.
How Do You Sharpen Circular Knife Blades?
Preparation
Clean The Blade: Remove any debris, resin, or leftover materials using a suitable cleaning agent.
Inspect The Blade: Check for any signs of excessive wear, cracks, or damage. If the blade is severely damaged, replacement may be more cost-effective.
Choose the Correct Sharpening Equipment
Grinding Machines: Use a dedicated blade grinding machine designed for circular blades, which ensures consistent sharpening angles and avoids over-grinding.
Grinding Wheel Selection: The choice of grinding wheel (diamond or abrasive) depends on the material composition of the blade. Carbide-tipped blades typically require a diamond wheel.
Sharpening Process
Set The Blade: Secure the blade in the grinding machine, ensuring it is stable and positioned correctly.
Adjust The Angles: Align the grinding machine to match the blade’s original bevel angle. Maintaining the correct angle is crucial for performance and longevity.
Coolant Application: Use coolant to prevent overheating and preserve the blade’s hardness.
Grinding: Carefully pass the grinding wheel over the blade’s edge in a consistent manner. This should be done gradually to avoid excessive removal of material.
Final Steps
Deburring: Remove any burrs that may form during the sharpening process to maintain a smooth, sharp edge.
Inspection And Testing: Check the blade for uniform sharpness and balance. Conduct a test cut if possible to ensure optimal performance.
How Long Do Circular Knife Blades Typically Last?
The lifespan of a circular blade isn’t fixed; it varies significantly based on key factors like the material being cut, the blade’s own composition, cutting speed, and overall operating conditions. The longevity figures provided below are general estimates for continuous operation under optimal conditions.

Carbide Circular Blades
These are known for their durability and can last between 50 to 100 hours of continuous operation under optimal conditions. They have high wear resistant, making them ideal for cutting hard materials or when consistent precision is needed.
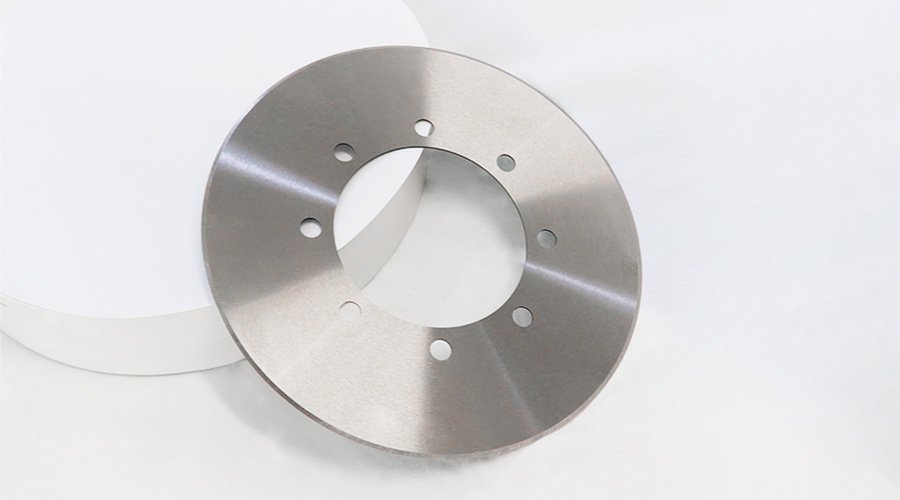

High-Speed Steel (HSS) Circular Blades
Depending on the application, these usually last 20 to 40 hours of use,. They are less durable than carbide blades but can still provide a good lifespan when used on softer materials.

Coated HSS Circular Blades
These HSS blades are enhanced with a ceramic coating, which boosts surface hardness and extends life well beyond standard HSS. They typically last 40 to 70 hours, offering a cost-effective upgrade for improved wear resistance.
Keep in mind that improper use, insufficient cooling, or cutting abrasive materials can greatly shorten a blade’s lifespan. Regular maintenance and proper use of the right blade for the cutting material can maximize efficiency and lifespan.







