Struggling with frequent blade changes and production downtime? The wrong blade material wears out fast, costing you time and money. What if you could find a blade that meets your specific cutting needs perfectly?
Tungsten carbide blades offer superior hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance, making them ideal for high-speed, continuous cutting. High-speed steel (HSS) blades provide better toughness1 and impact resistance2, excelling in applications with intermittent cuts or where the blade might face shocks and vibrations.
Choosing between tungsten carbide and high-speed steel is a common challenge for many of our clients. My client operated a large packaging factory and was extremely dissatisfied with the high-speed steel blades. They were cutting abrasive cardboard, and the blades dulled within hours, leading to constant machine stoppages. They saw the higher price of tungsten carbide as a barrier. I explained that while the initial cost is higher, the longer life and reduced downtime often lead to significant long-term savings. After they switched, their production efficiency soared. The "best" blade isn't about the price tag; it's about the right fit for the job. Let's explore the key differences to help you find that perfect fit.
Which Blade Stays Sharper Longer, Tungsten Carbide Or HSS?
Are your blades dulling too quickly, leading to rough cuts and wasted material? This constant wear forces frequent replacements, interrupting your workflow. The solution is finding a material that holds its edge under pressure.
Tungsten carbide blades stay sharper significantly longer than HSS blades due to their exceptional hardness. With a hardness rating3 typically between 89-94 HRA, tungsten carbide resists abrasive wear far better than HSS, which usually measures around 80-85 HRA, ensuring extended performance and precision.
When we talk about blade performance, hardness and wear resistance4 are the two most critical factors. A harder material can better withstand friction and abrasion, which directly translates to a longer-lasting sharp edge. I remember a client in the textile industry, let's call him Mr. Garcia from UK, who was cutting tough synthetic fabrics. His HSS blades were causing frayed edges after just a few hundred cuts. The abrasive nature of the material was grinding down the steel. We introduced him to tungsten carbide blades. He was hesitant about the cost, but we ran a trial. The carbide blade lasted thousands of cuts before needing any attention. The secret is in the material's composition.
Hardness and Material Composition
Tungsten carbide is a composite material made of hard carbide particles bonded together by a metallic binder, usually cobalt. This structure gives it incredible rigidity and resistance to deformation. High-speed steel, on the other hand, is an alloy of steel with elements like tungsten, molybdenum, and vanadium, which improve its hardness, but it remains fundamentally a steel alloy.
| Feature | Tungsten Carbide (TC) | High-Speed Steel (HSS) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HRA) | 89 - 94 | 80 - 85 |
| Primary Advantage | Extreme wear resistance | Good balance of hardness & toughness |
| Best For | Abrasive materials, long runs | General-purpose cutting |
| Weakness | Brittle, sensitive to impact | Softens at high temperatures |
This difference in hardness means that for applications involving plastics, paper, fiberglass, or composite materials, tungsten carbide is almost always the superior choice for longevity.
When Is High-Speed Steel A Better Choice Than Tungsten Carbide?
Have you ever installed a super-hard blade only to see it chip or shatter on the first heavy impact? Brittle materials can fail unexpectedly in tough conditions. You need a blade that can absorb shock without breaking.
High-speed steel is a better choice when toughness and impact resistance2 are more important than sheer hardness. Its superior flexibility allows it to handle interrupted cuts, heavy shocks, and vibrations without chipping, making it ideal for shearing thick metals or cutting non-uniform materials.
While tungsten carbide wins on hardness, HSS wins on toughness. Toughness is a material's ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing. This is where the inherent brittleness5 of carbide can be a disadvantage. I once cooperated with a metal recycling facility in Germany. They were using a large shear to chop scrap metal. They tried a carbide-tipped blade, hoping for longer life, but it chipped shortly after use because of the immense and unpredictable impact forces. I let he switched them to a high-quality HSS blade. It didn't stay sharp for as long, but it never fractured. It could be resharpened multiple times, making it the more reliable and cost-effective solution for their specific high-impact job.
Understanding Toughness vs. Brittleness
Think of it like glass versus a piece of rubber. Glass is very hard but shatters easily (brittle). Rubber is much softer but can be bent and stretched without breaking (tough).
- High-Speed Steel (HSS): Its steel-based structure gives it natural elasticity. It can flex slightly under load, which is crucial for absorbing the energy from a sudden impact. This makes it perfect for applications like guillotine shears or punching operations.
- Tungsten Carbide (TC): Its rigid, ceramic-like structure provides very little give. Any force that exceeds its structural limit will cause a fracture rather than a bend. This is why stable machine clamping and smooth, continuous cutting motions are so important when using carbide.
| Application Type | Recommended Material | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Interrupted Cuts | High-Speed Steel | Absorbs shock from material gaps |
| High Vibration | High-Speed Steel | Resists fatigue and fracture |
| Shearing Thick Metal | High-Speed Steel | Can handle immense impact forces |
| High-Precision, Stable Cutting | Tungsten Carbide | Holds edge for clean, continuous cuts |
So, if your machine has any vibration or the material you're cutting is inconsistent, HSS is often the safer and more reliable choice.
Is Tungsten Carbide Worth The Higher Initial Cost?
Worried that the high upfront price of tungsten carbide blades will hurt your budget? It’s tempting to choose the cheaper option to save money now. But what if that choice costs you more in the long run?
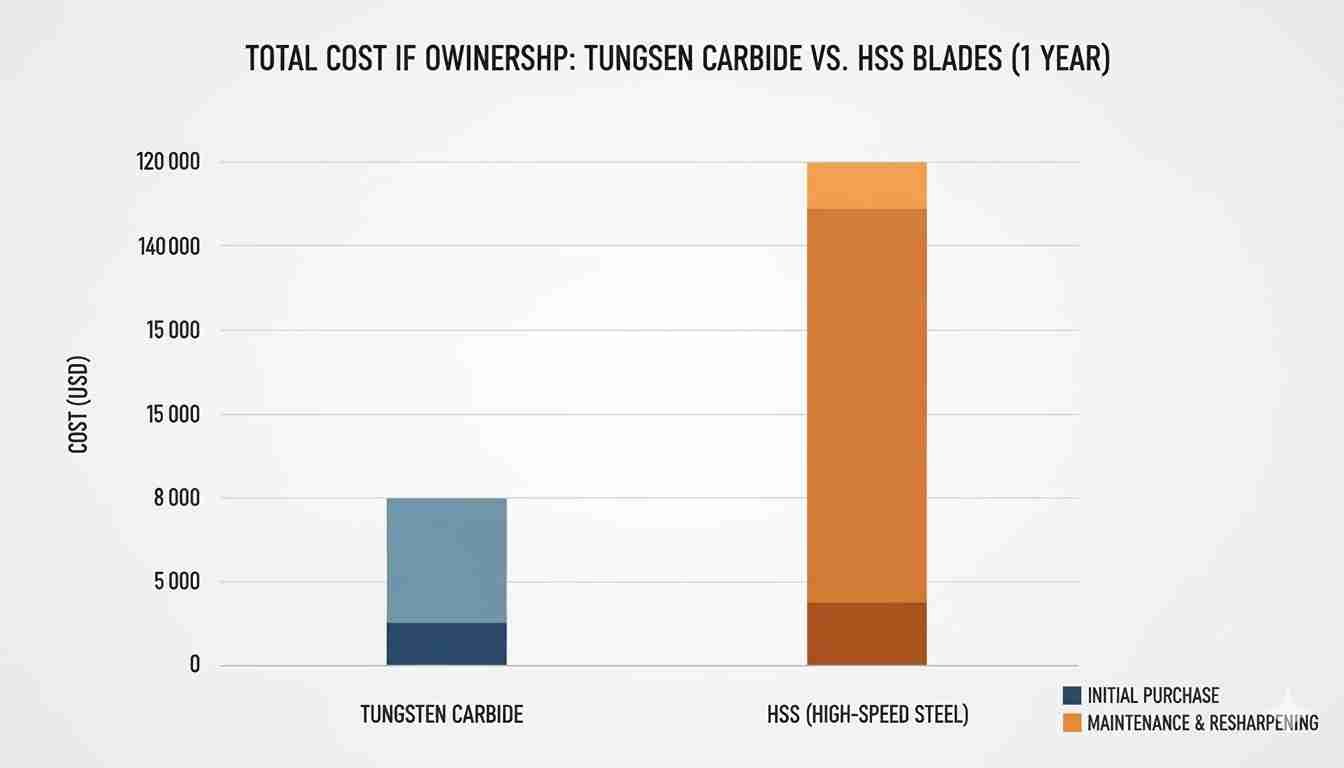
Yes, tungsten carbide is often worth the higher initial cost due to its much longer service life and reduced machine downtime. A single carbide blade can outlast many HSS blades, leading to a lower total cost of ownership, higher productivity, and better cut quality over time.
This is a conversation I have with customers almost every day. The sticker shock of a tungsten carbide blade can be significant compared to an HSS equivalent. However, true cost analysis goes beyond the purchase price. We must consider the total cost of ownership6 (TCO). Even though a tungsten carbide blade cost more, it lasted for more months.
Calculating the Total Cost of Ownership
Let's break down the factors that contribute to the total cost:
- Blade Price: The initial purchase price.
- Blade Lifespan: How long the blade lasts before needing replacement.
- Downtime Cost: The cost of lost production every time the machine is stopped for a blade change.
- Labor Cost: The cost of a technician's time to perform the blade change.
- Quality of Cut: The cost of wasted material due to dull blades.
| Cost Factor | High-Speed Steel (HSS) Example | Tungsten Carbide (TC) Example |
|---|---|---|
| Blade Price | $50 | $250 |
| Lifespan | 2 weeks | 24 weeks (6 months) |
| Blades per Year | 26 | ~2 |
| Annual Blade Cost | $1,300 | $500 |
| Downtime Events | 26 | 2 |
This simple example doesn't even include the cost of lost production during downtime, which is often the biggest expense. When you factor everything in, the more expensive blade is frequently the more economical choice for high-volume, continuous production environments.
Conclusion
Ultimately, choosing between tungsten carbide and HSS depends on your specific application. Tungsten carbide offers unmatched longevity for high-wear tasks, while HSS provides the toughness needed for high-impact jobs.
Discover the role of toughness in cutting tools and its impact on performance. ↩
Understand the importance of impact resistance in selecting blades for high-stress applications. ↩
Discover the significance of hardness ratings in selecting the right cutting blade for your needs. ↩
Find out how wear resistance can enhance the longevity and effectiveness of your cutting tools. ↩
Learn about brittleness in cutting tools and how it affects performance under stress. ↩
Learn how to calculate the total cost of ownership for cutting tools to make informed purchasing decisions. ↩